Frontpage News (3259)
Using tissue paper for menstruation unsafe, can cause infections
Site AdminA Senior Registrar of Gynaecology and Obstetrics at the Federal Medical Centre, Asaba, Dr. Daniel Adegbulu has advised women against using tissue paper in place of sanitary pads for menstruation, noting that it can cause severe infections.
Adegbulu explained that some tissue papers are made from waste papers which makes them a grave health risk for any woman who may be using them as a substitute for sanitary pads.
‘Stop asking for police report before treating gunshot victims’
Site AdminThe Lagos State Police Command has asked medical doctors to stop requesting a police report before treating gunshot victims. The Police Public Relations Officer in Lagos State, SP Benjamin Hundeyin, made this known in a tweet on his Twitter handle @benhundeyin.
He urged medical doctors to provide immediate medical attention to such victims before notifying the police. According to the Compulsory Treatment and Care of Victims of Gunshots Act, any hospital in Nigeria, whether public or private shall receive and accept for immediate treatment anyone with a gunshot wound.
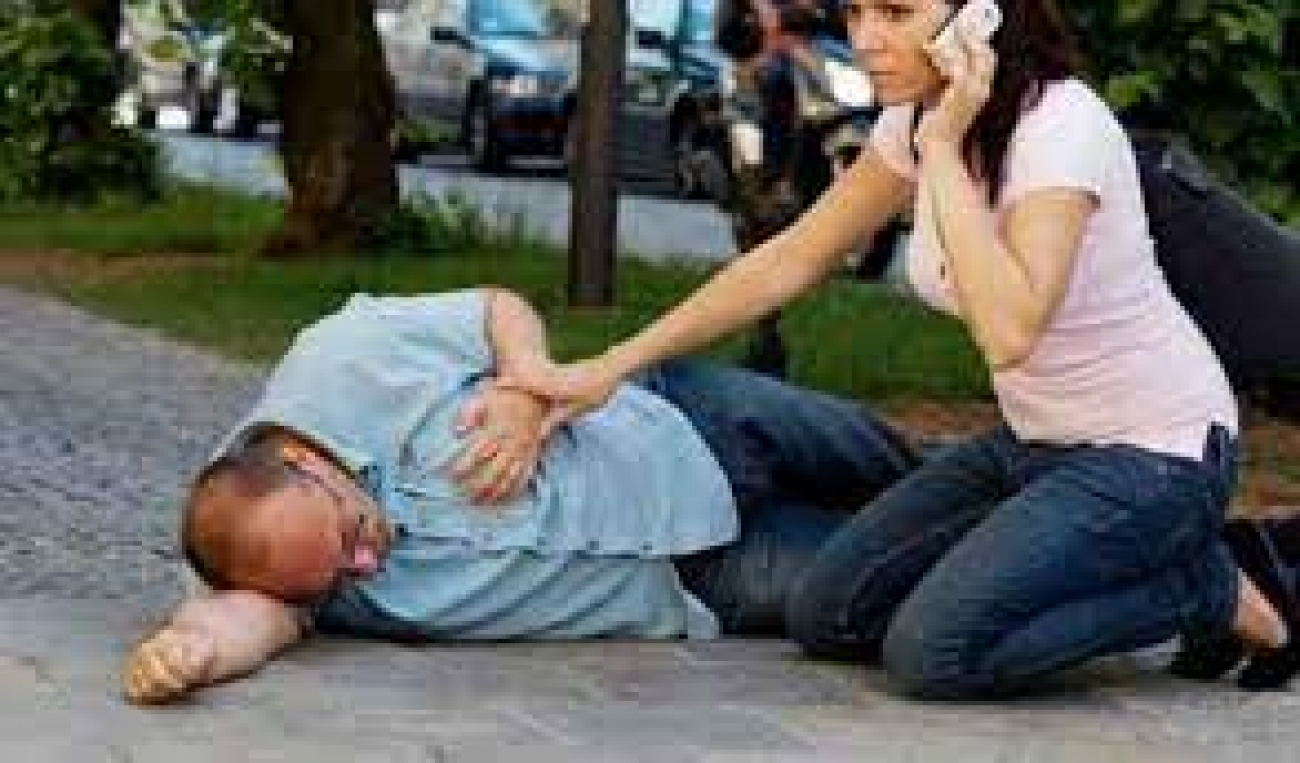
Uncontrolled blood pressure, low blood sugar, malaria can cause slumping to death –Cardiologist
Site AdminA heart care specialist, Dr. John Asekhame, has urged Nigerians to embrace regular health checks to reduce the increasing incidence of slumping and dying.
According to Asekhame, most cases of a sudden slump are not related to witchcraft or supernatural causes, but rather linked to undiagnosed and untreated cases of cardiac and non-cardiac health conditions.
NAFDAC warns Nigerians against drinking Japata Alcoholic Bitters
Site AdminThe National Agency for Food and Drug Administration and Control has warned Nigerians against the consumption of all variants of Japata Alcoholic Bitters 100 ml, an alcoholic drink produced by Chigodson International Company Limited.
The agency stated that laboratory findings have confirmed that Japata Alcoholic Bitters in circulation were contaminated, unwholesome, and unfit for humans to consume.
As soon as you have made up your mind that you want to have a baby, it is natural that you are hoping that it happens as soon as possible. Perhaps you know somebody who got pregnant easily, and you think you should too.
This is natural and you may likely get pregnant right away, or you may not. It’s important to know what is considered normal, so you don’t worry if there is no cause for concern. However, it is a fact that between 80 and 90 per cent of couples will conceive within 12 to 18 months of trying.
Piercing nipples can cause nerve damage, hepatitis B, experts warn
Site AdminHealth experts have cautioned Nigerian women against getting their nipples pierced, noting that engaging in the activity increases their risk of serious health complications in the short and long term.
According to the experts, the act can lead to certain damages such as blockage of the milk duct, nerve damage, pain, and bleeding. Nipple piercing, they warned, can also cause serious infections like hepatitis B, and HIV. The experts noted that piercing a nipple is not a medical procedure, adding that it is solely done for fashion.
A Professor of Clinical Neurology and Internal Medicine at the College of Medicine, University of Nigeria, Enugu, Ikenna Onwuekwe, has said that people with existing headaches are often more prone to having headaches when having sexual intercourse.
The health urged people who experience headaches during sex not to take it lightly but rather seek medical intervention from specialists. According to the neurologist, people who have migraine, tension, or fevers often experience a worsening of their headache when they engage in sex.
FG slams new tax on telephone calls to fund healthcare for vulnerable people
Site AdminThe Federal Government has slammed a new tax on phone calls in the nation to fund free healthcare for the Vulnerable Group in Nigeria. This is despite recent moves by telecommunication companies to increase the price of their services as a result of an unfavourable operating climate.
The telecom tax in the equivalent of a minimum of one kobo per second for phone calls is a part of the sources of funds required to finance free healthcare for the Vulnerable Group in Nigeria. This is contained in the National Health Insurance Authority Bill 2021 signed by the President, Major General Muhammadu Buhari (retd.), last week.
A medical health expert, Dr. Toluwani Binutu, has urged women with fishy-smelling vaginal discharge to seek medical intervention, noting that they could be infected with vaginosis – a bacterial infection.
Bacterial vaginosis, according to Mayo Clinic – a medical center focused on integrated health care, education, and research – is a type of vaginal inflammation caused by the overgrowth of bacteria naturally found in the vagina, which upsets the natural balance.
Teddy bears dangerous to children, can cause serious health problems, death, paediatrician warns
Site AdminA Consultant Paediatrician, Dr. Abdurrazzaq Alege, has cautioned parents against buying furry toys and teddy bears for their children, noting that they can cause serious health problems and even death for babies, especially infants.
According to the child health expert, babies exposed to fur are at risk of developing allergies, cough, suffocation, diarrhoea, and in some instances asthma.
More...
Why women should not wear underwear for more than 24 hours —Expert
Site AdminA Medical Laboratory Scientist, Obinna Chukwudi, has cautioned women against wearing underwear for more than 24 hours. According to the microbiologist, wearing underwear for more than 24 hours is not good for feminine hygiene.
The microbiologist who works at the Department of Microbiology, Nnamdi Azikiwe University Teaching Hospital, Nnewi, Anambra State, said the discharge and moisture buildup from the underwear provides a breeding ground for bacteria, and yeast infections contaminated with faecal and urine matter.
Smaller breasts can produce more milk for babies, physician says
Site AdminA medical health expert, Dr. Oluwatosin Kuku, has allayed the fears of women with small breasts who may be concerned that they may not produce enough breastmilk after childbirth, noting that the size of a woman’s breast has no role to play in the production of breastmilk.
According to the health expert, there’s no relationship between how a woman lactate and the size of her breast. She said, “In fact, a small breast can produce more milk than a big breast.”
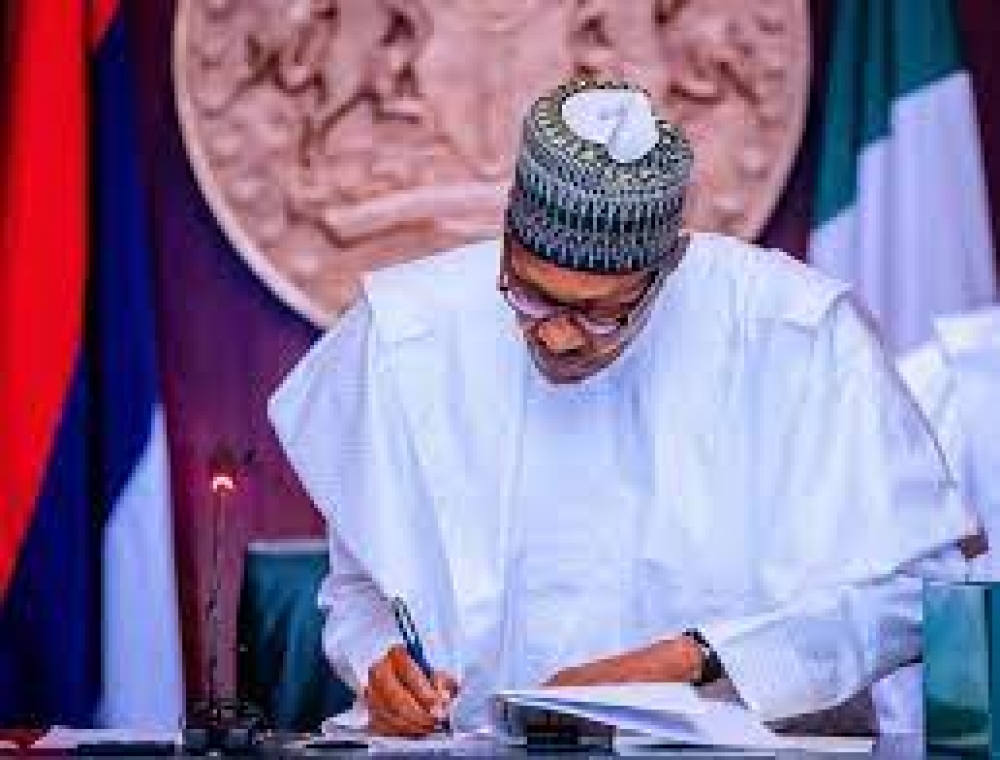
The President, Major General Muhammadu Buhari (retd.), has signed into law, the National Health Insurance Authority Bill 2022. The law repeals the National Health Insurance Scheme Act, Cap N42, Laws of the Federation of Nigeria 2004, according to a statement signed by the President’s Senior Special Assistant on Media and Publicity, Garba Shehu on Thursday.
Buhari said at the signing of the new law that a Fund will be set up “to ensure coverage of 83 million poor Nigerians who cannot afford to pay premiums as recommended by the Lancet Nigeria Commission.”
Teething doesn’t cause fever, diarrhoea in babies, paediatrician tells mothers
Site AdminA child health expert, Prof. Edamisan Temiye, has said that it is untrue that teething causes fever and diarrhoea in babies. According to the paediatrician, it is an infection that usually causes fever in children and not teething, noting that teething is a natural thing.
He said that some mothers have the misconception that teething in babies is associated with some symptoms, especially fever and diarrhoea. Prof. Temiye who is a Consultant Paediatric Haematologist and Oncologist at the Lagos University Teaching Hospital, Idi-Araba, said teething does not cause a problem for any baby.