Nigerians consume 20 billion sticks of cigarette annually – Minister
 Over 20 billion sticks of cigarettes are consumed annually in Nigeria, the Minister of Health, Isaac Adewole, has said. Mr. Adewole also said 4.5 million adults currently use tobacco products, while about 82 percent of people who visit bars and nightclubs are exposed to second-hand smoke.
Over 20 billion sticks of cigarettes are consumed annually in Nigeria, the Minister of Health, Isaac Adewole, has said. Mr. Adewole also said 4.5 million adults currently use tobacco products, while about 82 percent of people who visit bars and nightclubs are exposed to second-hand smoke.
The minister, who spoke during a press briefing organized to mark the 2018 World No-Tobacco day celebration in Abuja on Monday, said in 2015, the country’s projected accumulated loss to tobacco was put at $7.6 billion.
Funding: Nigeria’s Health Sector In State of Emergency – Lawmaker
 The Chairman, Senate Committee on Health, Lanre Tejuosho disclosed this while explaining various shortfalls bedeviling the funding of the health industry at the commemoration of MAMAYE day 2018 in Abuja.
The Chairman, Senate Committee on Health, Lanre Tejuosho disclosed this while explaining various shortfalls bedeviling the funding of the health industry at the commemoration of MAMAYE day 2018 in Abuja.
The theme of the event is ‘Improving Nigeria’s Health Budget Performance’.
TB kills over 1.6m people annually – UN
 The UN has said no fewer than 1.6 million people are killed annually by tuberculosis and the disease would cost about one trillion dollars in the economic loss by 2050.
The UN has said no fewer than 1.6 million people are killed annually by tuberculosis and the disease would cost about one trillion dollars in the economic loss by 2050.
“Despite being curable and treatable, TB kills more than 1.6 million people every year and only about half the cases are diagnosed properly. “The disease also takes an enormous financial toll on economies: it is estimated that TB will cost about one trillion dollars by 2030,” the UN said.
LUTH Records High Patient Turnout After JOHESU Strike
 Activities have started picking up at the Lagos University Teaching Hospital (LUTH) in Idi-Araba. This followed the end of the strike by the Joint Health Sector Union (JOHESU).
Activities have started picking up at the Lagos University Teaching Hospital (LUTH) in Idi-Araba. This followed the end of the strike by the Joint Health Sector Union (JOHESU).Nigeria Needs N14.4b to Control TB as 420 Die Daily
 The Coordinator, National Tuberculosis and Leprosy Control Programme, Dr. Adebola Lawanson, yesterday disclosed in Abuja that 420 Nigerians die every day due to tuberculosis.
The Coordinator, National Tuberculosis and Leprosy Control Programme, Dr. Adebola Lawanson, yesterday disclosed in Abuja that 420 Nigerians die every day due to tuberculosis.Nigerian govt increases maternity leave to four months
 The Nigerian government has increased maternity leave to four months. Under the Nigerian Labour Law passed in 2004, a woman working in the country’s civil service has the right to maternity leave of three months, as long as she provides a medical certificate stating she should not or cannot work.
The Nigerian government has increased maternity leave to four months. Under the Nigerian Labour Law passed in 2004, a woman working in the country’s civil service has the right to maternity leave of three months, as long as she provides a medical certificate stating she should not or cannot work.
The medical certificate allows her to stay off work for 12 weeks – six weeks before the birth of her baby and six weeks after.
DR Congo approves use of five new Ebola drugs – WHO
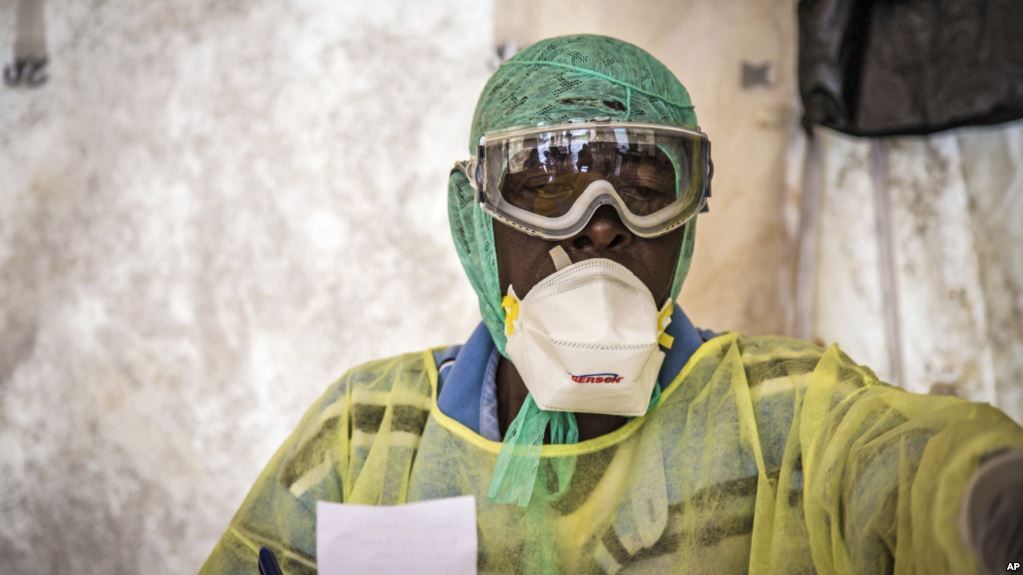 The Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) has approved the use of five investigational therapeutics to treat Ebola Virus Disease (EVD), marking the first time such treatments have been available in the midst of an Ebola outbreak in the country, the WHO said.
The Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) has approved the use of five investigational therapeutics to treat Ebola Virus Disease (EVD), marking the first time such treatments have been available in the midst of an Ebola outbreak in the country, the WHO said.
The WHO said four of the five approved drugs are currently in the country, which are Zmapp, GS-5734, REGN monoclonal antibody combination, and mAb114, under the framework of compassionate use and expanded access.
Cannabis oil cures stomach cancer as new genetic diagnosis
 A new prostate cancer Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA)/genetic material test identifies the one in 100 men who are six times more at risk of developing the life-threatening disease. Researchers identified 63 new genetic mutations that are linked to the condition, which they combined with more than 100 DNA variants that were already known to cause the condition, to create the test, which could cost as little as £30.
A new prostate cancer Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA)/genetic material test identifies the one in 100 men who are six times more at risk of developing the life-threatening disease. Researchers identified 63 new genetic mutations that are linked to the condition, which they combined with more than 100 DNA variants that were already known to cause the condition, to create the test, which could cost as little as £30.
The findings were published in the journal Nature Genetics. One percent of men carry many of these risky genetic variations, putting them at a much higher risk of prostate cancer than the average male, a study found today. These DNA mutations tend to occur in cells that regulate communication between the immune system and other parts of the body, which could pave the way for new treatments, according to the researchers.
Artificial kidney breakthrough
 A coffee cup-sized implant that mimics the functions of the human kidney could be a life-saving option for patients with chronic kidney disease. According to DailyMail UK Online, the implant is expected to begin trials later this year and if successful, it could be available within a few years, saving patients from dialysis or needing a transplant —there are currently 30,000 people in the United Kingdom (UK) having dialysis, and 5,000 on the waiting list for a donor kidney.
A coffee cup-sized implant that mimics the functions of the human kidney could be a life-saving option for patients with chronic kidney disease. According to DailyMail UK Online, the implant is expected to begin trials later this year and if successful, it could be available within a few years, saving patients from dialysis or needing a transplant —there are currently 30,000 people in the United Kingdom (UK) having dialysis, and 5,000 on the waiting list for a donor kidney.
How Medical Laboratories Accreditation Helps In Healthcare Delivery
 Mr Tosan Erhabor, the Acting Registrar, Medical Laboratory Science Council of Nigeria (MLSCN), says accreditation of medical laboratories in Nigeria is key to delivering safer results. Erhabor said this at the commemoration of 2018 World Accreditation Day in Abuja on Tuesday also said accreditation of medical laboratories saves lives.
Mr Tosan Erhabor, the Acting Registrar, Medical Laboratory Science Council of Nigeria (MLSCN), says accreditation of medical laboratories in Nigeria is key to delivering safer results. Erhabor said this at the commemoration of 2018 World Accreditation Day in Abuja on Tuesday also said accreditation of medical laboratories saves lives.
This year’s theme is: “Accreditation: Delivering A Safer World”.